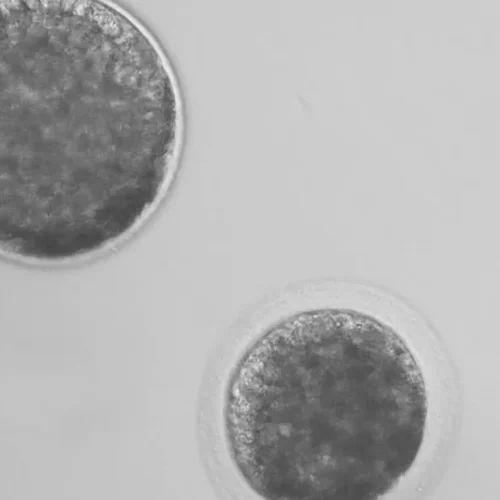
Animal cloning is a reproductive technique that enables the creation of individuals that are almost genetically identical. This technique has been used in various fields such as medicine, agriculture, and livestock (research). In the field of equestrian sports, animal cloning is becoming an increasingly popular tool.
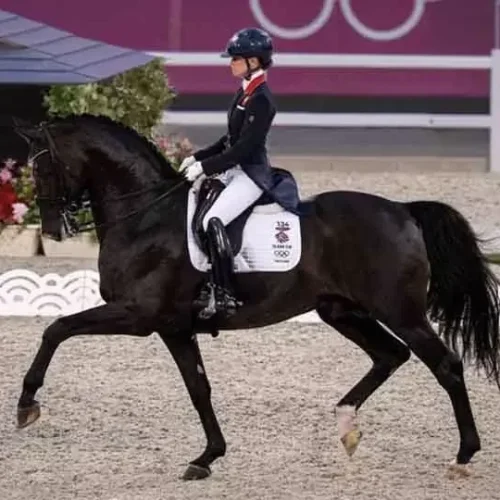
Recently, “Otterongo Alpha Z”, a cloned horse, won the CSI5*-W 1.55m Grand Prix in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. “Otterongo Alpha Z” is a 9-year-old KWPN horse. The original horse, “Otterongo van de Kopshoeve”, had a remarkable sporting career. He won numerous Grand Prix events, including a 4th place at the 2000 Sydney Olympics.
The cloning of “Otterongo van de Kopshoeve” was performed by a team of scientists from Utrecht University in the Netherlands. The team used a cloning technique known as somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT). This technique involves transferring the nucleus of a somatic cell from an animal into an enucleated recipient oocyte. The resulting embryo is then transferred to a surrogate mare.
Cloning makes it possible to create horses that are almost genetically identical to other highly valuable horses. This can help breeders and riders produce horses with the desired traits for equestrian performance.